Difficulty Level: Beginner – Basic User
Experiencing slow Wi-Fi can be incredibly annoying, especially when your video call freezes or your streaming app starts buffering. Because more homes today rely on multiple devices, weak Wi-Fi signals have become a common frustration. When these issues appear, many people consider either Mesh Wi-Fi or Wi-Fi Extenders. Although both promise better coverage, they work very differently and deliver very different results. Therefore, understanding how each one behaves will help you choose a long-lasting solution instead of wasting money on the wrong upgrade.
Key Takeaway
Mesh WiFi = Seamless home-wide coverage
WiFi Extender = Budget fix for one or two weak areas
Mesh WiFi vs Extender — Understanding the Core Difference
Both technologies aim to extend coverage, however, their performance varies significantly because of the way each system handles wireless signals. As a result, your experience can change dramatically depending on which option you install.
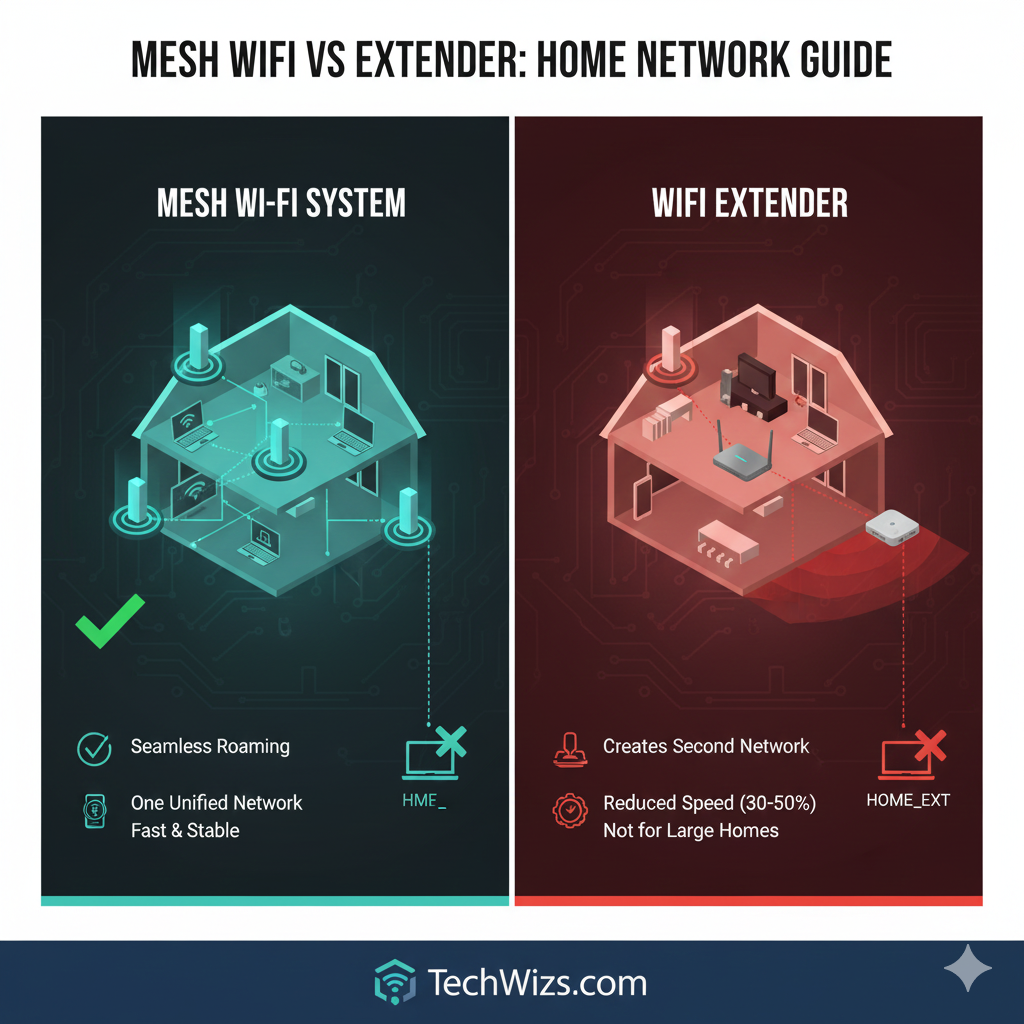
What Is Mesh WiFi? (Unified, Stable Coverage)
A Mesh Wi-Fi system uses several coordinated nodes that communicate with each other to create one large, unified network. Think of it like having multiple “mini routers” working together as one big team. This arrangement means your device always connects to the closest and strongest node automatically.
Mesh systems, furthermore, distribute the workload instead of relying on a single router. They adjust automatically when obstacles or walls interfere with the signal. Consequently, this design ensures stronger performance in modern homes filled with smart devices.
Mesh WiFi advantages:
- One network name everywhere
- Seamless roaming between nodes
- Better speed consistency
- Excellent for multi-floor homes
According to TP-Link, mesh systems can increase usable Wi-Fi coverage by up to 250% compared to standard routers.
What Is a WiFi Extender? (Simple but Limited Boost)
A Wi-Fi extender repeats your router’s existing signal to reach distant areas. In contrast, it broadcasts a second Wi-Fi name, which means your devices must manually switch networks when you move around the house. Additionally, extenders divide signal strength, causing speeds to often drop.
Therefore, performance feels weaker during tasks such as streaming, gaming, or online meetings. Although extenders help cover small gaps, nonetheless, they rarely deliver reliable whole-home stability.
Extender limitations:
- Creates a second Wi-Fi name (example: Home_EXT)
- Can reduce speed by 30–50%
- Struggles with thick walls
- Not ideal for large homes
Still, extenders can be a quick and inexpensive solution for small apartments.
Mesh WiFi vs Extender — How to Choose the Right Option
Choosing the correct setup depends heavily on your home size, construction materials, and daily internet activities. Because each environment behaves differently, the guide below offers a clear approach for every scenario.
For Small Homes or Apartments (Under 1,000 sq ft)
A strong standalone router usually performs well in smaller spaces. If you only have one or two weak spots, an extender is fine. Generally, apartments also have fewer walls, making extenders more efficient.
For Medium Homes (1,000–2,500 sq ft)
Mesh Wi-Fi performs noticeably better in this range. Medium homes often include long hallways, more devices, and several rooms competing for Wi-Fi coverage. With a two-node mesh system, however, your home receives consistent performance without frustrating disconnects.
For Large or Multi-Story Homes (2,500+ sq ft)
A mesh system is the best choice here. Concrete walls, staircases, and long distances weaken extender performance significantly. Since mesh nodes communicate actively, they maintain strong coverage across floors. Consequently, mesh becomes the only truly reliable option in complex layouts.
For Gamers, 4K Streamers, and Remote Workers
Mesh Wi-Fi is strongly recommended because tasks like gaming and video conferencing require stability. Extenders typically struggle to deliver low latency, so mesh provides a noticeably smoother experience. Furthermore, mesh systems handle dozens of devices simultaneously without slowing down.
Side-by-Side Comparison: Mesh WiFi vs WiFi Extender
| Feature | Mesh WiFi System | WiFi Extender |
| Speed | Consistent and fast | Often 30–50% slower |
| Network Name | One unified SSID | Creates a second SSID |
| Roaming | Smooth and seamless | Interrupted when switching |
| Coverage | Ideal for medium–large homes | Limited to small spots |
| Stability | Excellent | Moderate |
| Setup Difficulty | Very easy | Easy |
| Best For | Whole-home reliability | Budget-based improvements |
| Price | Higher | Low |
| Gaming/4K Streaming | Excellent | Poor–Moderate |
| Smart Homes | Very reliable | Can cause device disconnections |
Recommended Hardware — Best Mesh & Extender Options
Best Mesh WiFi for Large Homes
- TP-Link Deco X55 (WiFi 6) – Affordable and stable
- ASUS ZenWiFi AX Mini – Simple app control
- Google Nest WiFi Pro – Extremely user-friendly
Best Mesh WiFi for High-Speed Power Users
- ASUS ZenWiFi XT8 – Strong performance with dedicated backhaul
- Netgear Orbi RBK752 – Excellent long-range stability
Best WiFi Extenders (Budget)
- TP-Link RE605X (WiFi 6) – Fast and compact
- Netgear EX6120 – Budget-friendly and effective
- Linksys RE7000 – Good coverage with minimal setup
How to Choose WiFi Equipment (Specs That Matter)
Important Features to Check
Selecting the right hardware ensures long-term stability. Therefore, consider the following:
- WiFi Version: Choose WiFi 6 or WiFi 6E for better performance
- Backhaul Type: Mesh with Ethernet or dedicated wireless backhaul is best
- LAN Ports: Useful for consoles, NAS, or TV streaming
- Coverage Rating: Aim for 1,500 sq ft per mesh node
Easy Rule of Thumb
- Many walls or multiple floors → Choose Mesh WiFi
- Small homes with only one weak spot → Extender works fine
- Gamers and streamers → Mesh is almost always better
Real-World Scenarios
Scenario 1: Small Apartment User
A couple struggles with weak Wi-Fi in one corner.
- Recommended solution: One extender or a better standalone router.
Scenario 2: Two-Story Family Home
Family with 3 kids, smart TVs, PlayStation, and 20+ devices.
- Recommended solution: A 2–3 node Mesh WiFi (Deco X55).
Scenario 3: Work-from-Home + Gaming
A user experiences lag while moving between floors.
- Recommended solution: Mesh WiFi with Ethernet backhaul.
FAQ — Mesh WiFi vs Extenders
Is an extender good for gaming?Not recommended. Instead, mesh delivers lower latency and more stability.
Does Mesh WiFi increase internet speed?Mesh does not raise your ISP speed, but it ensures your full speed reaches more rooms.
Why do extenders slow down?Extenders re-broadcast your router’s signal, which divides bandwidth and consequently reduces performance.
Can I keep my old router when using mesh?Yes. However, many mesh systems work best when your old router is switched to Access Point mode.
Is mesh difficult to install?Very easy. Most systems complete setup in under 10 minutes.
How many mesh nodes do I need?1,000–2,000 sq ft → 2 nodes2,500–3,500 sq ft → 3 nodes