Difficulty: Beginner
What Is a Monitor Refresh Rate?
Definition Box – Refresh Rate (Hz)
A monitor’s refresh rate, measured in Hertz (Hz), indicates how many times the display refreshes the image every second.
Example: 60Hz = 60 refreshes per second.
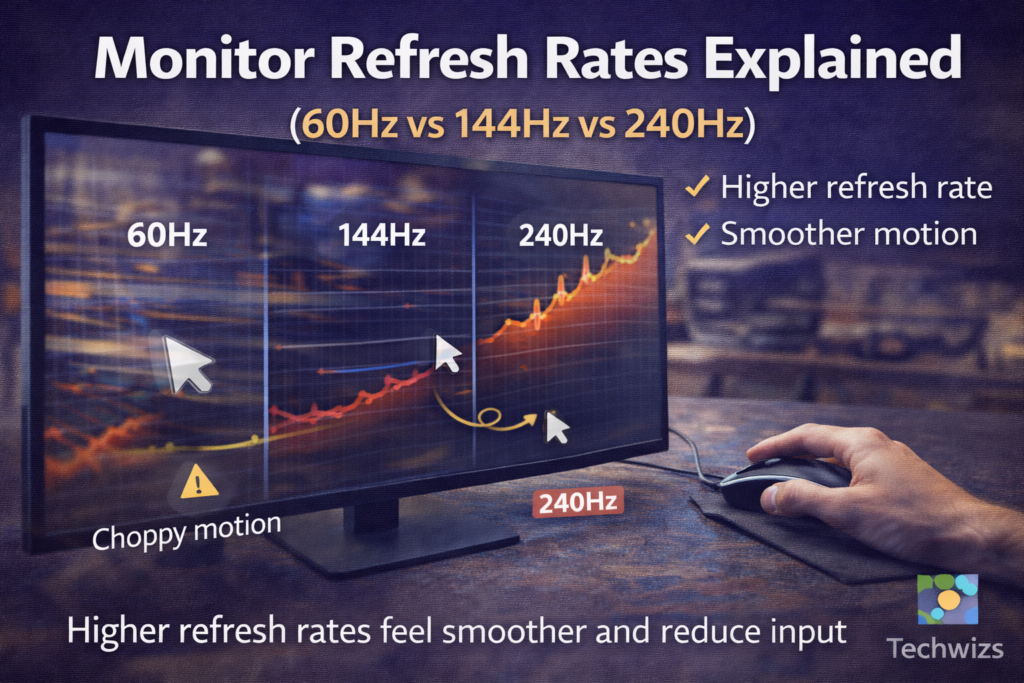
The higher the refresh rate, the smoother motion appears on screen. However, smoother visuals only happen if your computer can actually deliver enough frames per second (FPS).
Why Monitor Refresh Rates Matter
Refresh rates influence:
- Motion smoothness
- Scrolling clarity
- Responsiveness
- Eye comfort (for some users)
According to display technology data referenced by manufacturers like NVIDIA and DisplayPort standards bodies, higher refresh rates reduce perceived motion blur and input lag—especially in fast-moving scenes.
Key Takeaway Box
A higher refresh rate doesn’t just help gamers—it can make everyday screen use feel noticeably smoother.
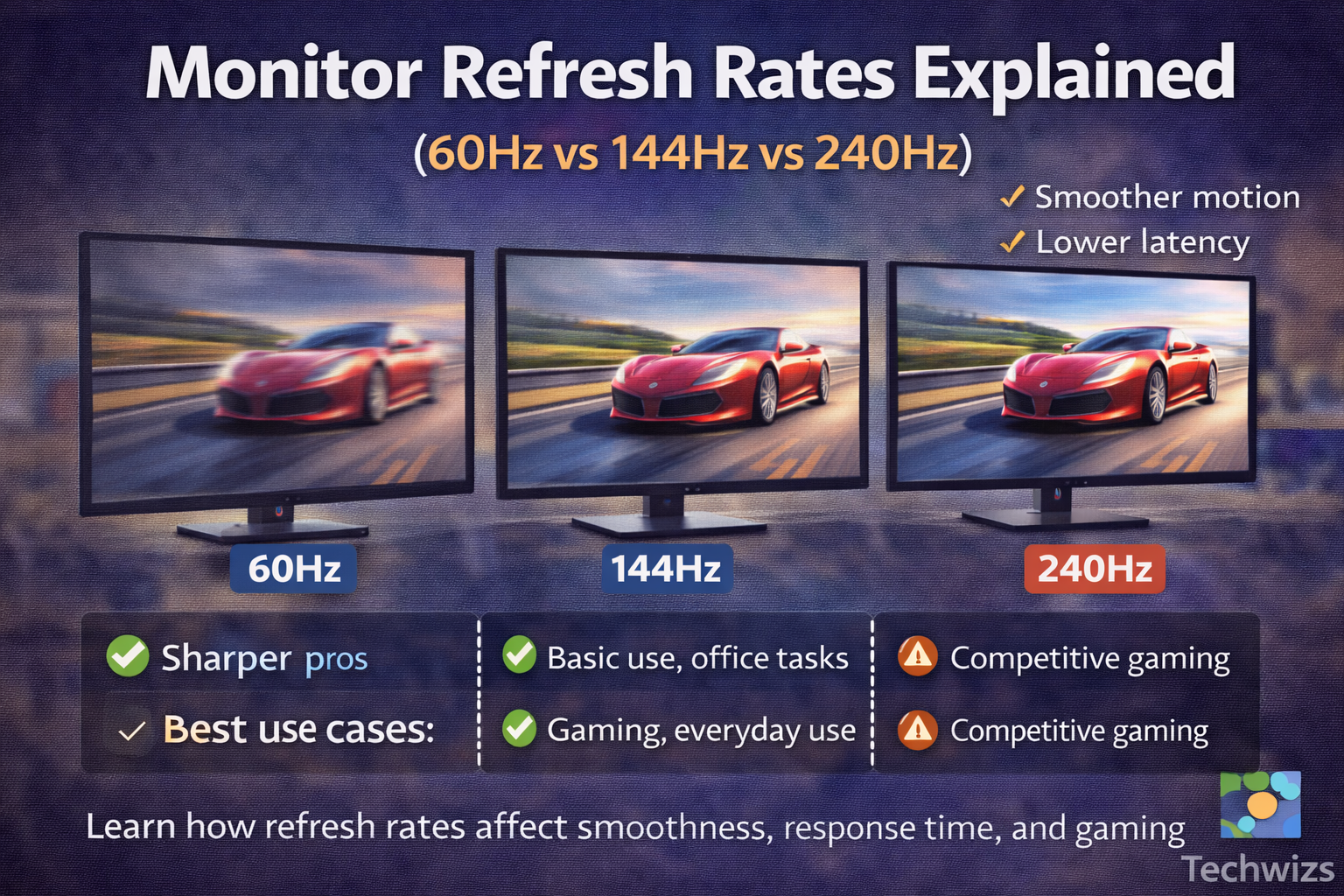
60Hz Monitors: Who Are They For?
What 60Hz Feels Like
- Standard motion smoothness
- Slight blur during fast scrolling
- Minor delay in fast cursor movement
Best use cases:
- Office work
- Web browsing
- Email and documents
- Watching videos (most videos are 24–60 FPS)
Pros:
- Cheapest option
- Low system requirements
- Widely available
Cons:
- Less smooth scrolling
- Not ideal for gaming
- Feels sluggish once you’ve used higher refresh rates
144Hz Monitors: The Sweet Spot
For many users, 144Hz is the best balance between performance and price.
What 144Hz Feels Like
- Much smoother scrolling
- Noticeably better motion clarity
- More responsive mouse movement
Best use cases:
- Gaming (casual to competitive)
- Programming and multitasking
- Video editing timelines
- General daily use (once you try it, it’s hard to go back)
Pros:
- Big improvement over 60Hz
- Widely supported by modern GPUs
- Reasonable pricing in 2025
Cons:
- Requires stronger hardware to fully benefit
- Uses more power than 60Hz
Quick Fix Box
If you want one monitor that feels smooth for everything, 144Hz is usually the safest upgrade.
240Hz Monitors: Who Actually Needs Them?
What 240Hz Feels Like
- Extremely smooth motion
- Minimal motion blur
- Ultra-responsive feel
Best use cases:
- Competitive esports
- High-FPS gaming (CS2, Valorant, Apex)
- Users with powerful GPUs and CPUs
Pros:
- Lowest perceived input lag
- Best motion clarity available
- Competitive advantage in fast games
Cons:
- Expensive
- Requires very high FPS to matter
- Minimal benefit for office work or media consumption
For most people, the jump from 144Hz to 240Hz is far less noticeable than the jump from 60Hz to 144Hz.
60Hz vs 144Hz vs 240Hz: Quick Comparison
| Refresh Rate | Smoothness | Best For | Worth It? |
|---|---|---|---|
| 60Hz | Basic | Office, media | ✅ Yes (budget) |
| 144Hz | Very smooth | Gaming, daily use | ✅✅ Best value |
| 240Hz | Ultra-smooth | Competitive gaming | ⚠️ Niche |
Does Your PC Matter?
A high-refresh monitor won’t help much if your PC can’t push enough frames.
Rule of thumb:
- 60Hz → 60 FPS
- 144Hz → 100–144 FPS
- 240Hz → 180–240 FPS
If your system struggles to hit those numbers, the benefits drop significantly.
Refresh Rate vs Resolution (Common Mistake)
Many buyers face this choice:
- Higher refresh rate or
- Higher resolution
General advice:
- Office & productivity → higher resolution
- Gaming & motion → higher refresh rate
- Balanced use → 144Hz at 1080p or 1440p
Is Higher Refresh Rate Better for Your Eyes?
Higher refresh rates can:
- Reduce perceived flicker
- Make motion easier to track
- Reduce eye strain for some users
However, eye comfort also depends on:
- Brightness
- Blue light settings
- Viewing distance
- Break habits
FAQ: Monitor Refresh Rates
Is 144Hz worth it over 60Hz?
Yes. Most users notice an immediate improvement in smoothness.
Can I use a 144Hz monitor for office work?
Absolutely. Scrolling and cursor movement feel smoother.
Is 240Hz overkill?
For most people, yes—unless you play competitive esports seriously.
Does refresh rate affect video playback?
Not significantly. Most videos play at 24–60 FPS.
Will higher refresh rates reduce input lag?
Yes. Higher refresh rates reduce perceived input delay.







