Difficulty: Beginner
What’s the Real Difference Between Ethernet and Wi-Fi?
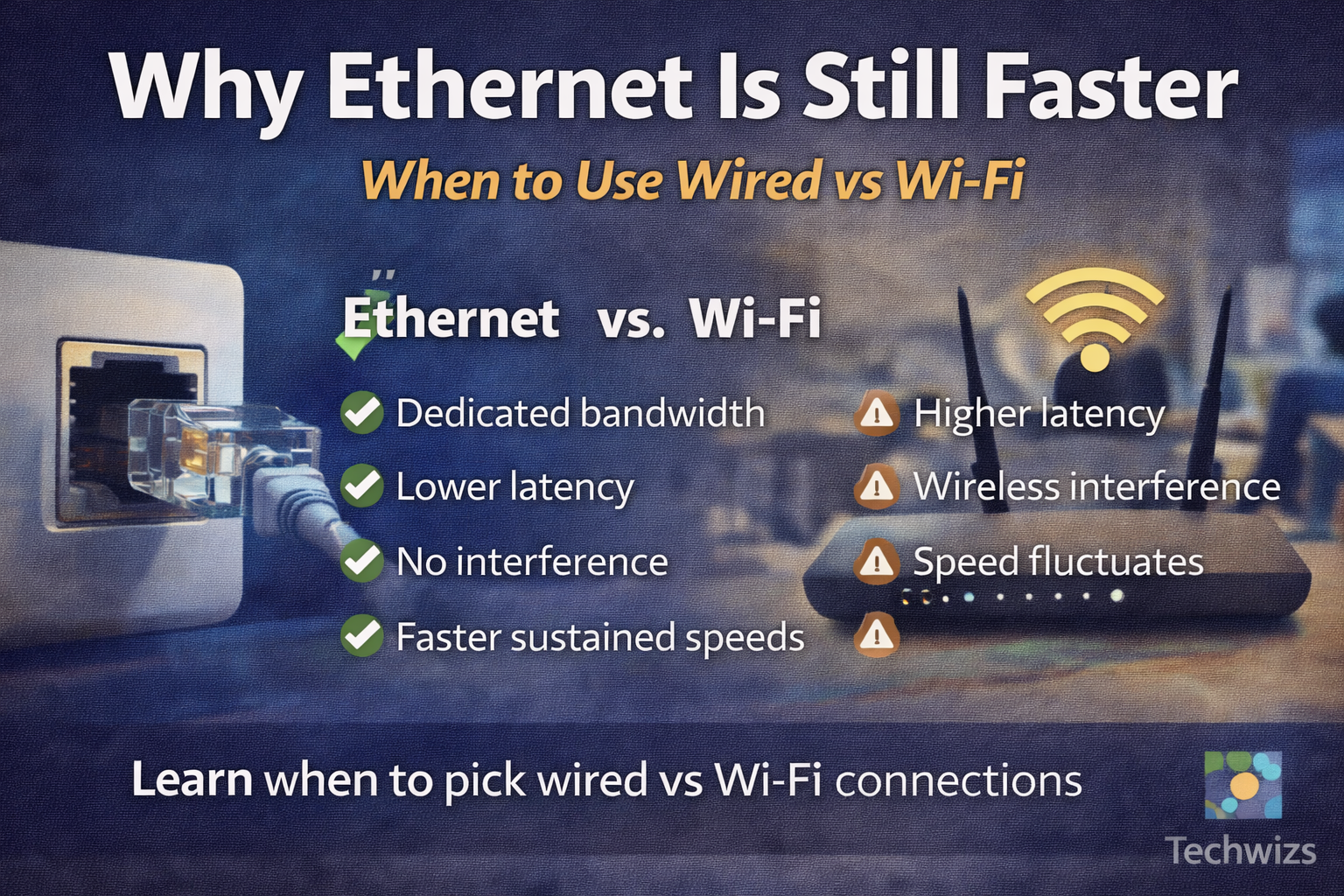
Definition Box – Ethernet vs Wi-Fi
Ethernet uses physical cables to connect devices directly to a network.
Wi-Fi, on the other hand, sends data wirelessly using shared radio signals.
At a basic level, the difference seems simple. However, that distinction explains why performance varies so much between the two.
With Ethernet, your device has a direct line to the router or switch. Wi-Fi, by contrast, shares bandwidth with every nearby device using the same signal.
Why Ethernet Is Still Faster Than Wi-Fi
1. Dedicated Bandwidth Means Consistent Speed
Ethernet connections are not shared with other devices. As a result, your speed remains stable regardless of how many phones or laptops are nearby.
Wi-Fi behaves differently. Because multiple devices compete for the same airwaves, performance drops as usage increases. For this reason, crowded networks often feel slow even with fast internet plans.
Key Takeaway Box
Ethernet stays fast because no other devices compete for your cable.
2. Lower Latency Improves Real-Time Performance
Latency refers to how quickly data travels back and forth. In comparison, Ethernet delivers lower and more predictable latency than Wi-Fi.
This difference becomes obvious during:
- Video conferencing
- Online gaming
- Remote desktop sessions
- VoIP calls
Even small latency spikes can cause lag or dropped audio. That’s why professionals still rely on wired connections whenever timing matters.
3. No Interference From the Environment
Wi-Fi signals weaken due to walls, distance, and nearby electronics. Meanwhile, Ethernet cables are immune to these problems.
In busy homes or offices, wireless interference increases packet loss. According to IEEE networking standards, wired connections experience significantly fewer transmission errors in dense environments.
4. Real-World Speeds vs Advertised Speeds
Although Wi-Fi standards advertise impressive numbers, those speeds are theoretical. In reality, actual performance fluctuates constantly.
Ethernet speeds—such as 1Gbps or 2.5Gbps—are sustained and measurable. As a result, wired connections feel faster and more reliable during everyday tasks.
When You Should Use Ethernet (Wired)
Ethernet is still the best choice when stability matters more than mobility.
Use Ethernet if you:
- Work from home or in an office
- Transfer large files or backups
- Rely on VPNs or cloud services
- Game or stream competitively
- Run servers or network storage
In these cases, reliability outweighs convenience.
When Wi-Fi Makes More Sense
Despite its limits, Wi-Fi remains essential.
Wi-Fi works best when:
- You need mobility
- Running cables isn’t practical
- Your tasks are lightweight
- You use phones or tablets
Quick Fix Box
Use Wi-Fi for convenience and Ethernet for performance.
Is Modern Wi-Fi Catching Up?
New standards like Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 7 have narrowed the gap. Even so, wireless connections still share bandwidth and remain vulnerable to interference.
As a result, Ethernet continues to be the gold standard for consistency—especially in professional environments.
Common Myths About Ethernet vs Wi-Fi
❌ “My Wi-Fi speed test is fast, so Ethernet isn’t needed”
Speed tests don’t reveal latency stability or packet loss. Therefore, they don’t tell the full story.
❌ “Ethernet is outdated”
In reality, Ethernet standards keep evolving and now support multi-gigabit speeds.
❌ “Wi-Fi is just as reliable”
While Wi-Fi has improved, wired connections remain more dependable overall.
The Best Setup: Wired and Wireless Together
Rather than choosing one, smart setups use both.
For example:
- Ethernet for desktops, TVs, and consoles
- Wi-Fi for mobile devices
- Wired backhaul for mesh systems
This hybrid approach balances speed, reliability, and flexibility.
FAQ: Ethernet vs Wi-Fi (Schema Ready)
Is Ethernet always faster than Wi-Fi?
In real-world use, Ethernet is usually faster and more consistent.
Does Ethernet improve internet speed?
It improves stability and latency, which often feels like higher speed.
Is Ethernet safer than Wi-Fi?
Yes. Wired connections are harder to intercept.
Should I use Ethernet for work laptops?
If you work remotely or attend frequent calls, Ethernet is recommended.
Will Ethernet become obsolete?
Unlikely. Wired networking remains essential for performance-critical tasks.








